2/28/2014: Notebook Assignment #2
Scientists use all sorts of models to help explain their ideas. They also make models to try out designs on a small scale before building something that will be very large and expensive. If the model works well, they can use it to raise the money they need to build the true thing. Conversely, If something is too small to see easily, scientists may make an enlarged model so that they can manipulate it easily. This may help them figure out how the smaller thing behaves. Another way that scientists use models is to make predictions about the future.
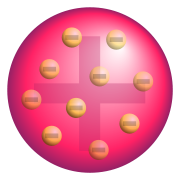
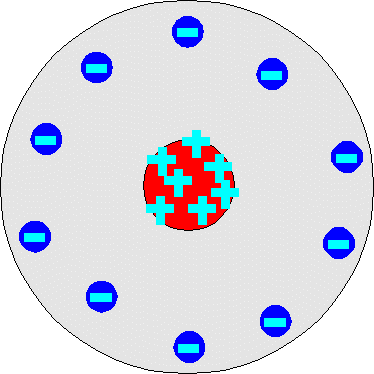
Each of the scientists above created a model of the atom based on their discovery and previous discoveries from other scientists. From what you know about their discoveries, try to match each scientist to their model.
Draw their models and the model name associated with each scientist in your notes on that scientist.
Scientists use all sorts of models to help explain their ideas. They also make models to try out designs on a small scale before building something that will be very large and expensive. If the model works well, they can use it to raise the money they need to build the true thing. Conversely, If something is too small to see easily, scientists may make an enlarged model so that they can manipulate it easily. This may help them figure out how the smaller thing behaves. Another way that scientists use models is to make predictions about the future.
Each of the scientists above created a model of the atom based on their discovery and previous discoveries from other scientists. From what you know about their discoveries, try to match each scientist to their model.
Draw their models and the model name associated with each scientist in your notes on that scientist.
3/4/2014: Quiz
Quiz#1: History of the Atom
This quiz contains information on each of the scientists, their discoveries, and their Atomic Models. It also has the first 10 elements and their names/symbols. It is 30 questions: matching, true and false, and multiple choice. The access code will be given to you in class.
3/26/2014: Quiz
Quiz #2: Electron Configurations and Periodic Properties
This quiz is an open note quiz that contains material from Chapter 5 sections 2 and 3. The access code will be given to you in class.
Quiz#1: History of the Atom
This quiz contains information on each of the scientists, their discoveries, and their Atomic Models. It also has the first 10 elements and their names/symbols. It is 30 questions: matching, true and false, and multiple choice. The access code will be given to you in class.
3/26/2014: Quiz
Quiz #2: Electron Configurations and Periodic Properties
This quiz is an open note quiz that contains material from Chapter 5 sections 2 and 3. The access code will be given to you in class.
Notebook Assignment #3Go to the following website and take notes from the animation. Add these notes to "Rutherford and the Nucleus" in your notebook.
Rutherford's Gold Foil Experiment |
Lab 1Using the background information that you have gathered about the Gold Foil Experiment it is now time to try it on your own. Read through the instructions show here. Go to the webiste for Rutherfords Scattering and complete Excercises 1 and 2 using the animation. Answer all of the questions in your notebook.
|
||||||
Review for Unit 5 Test: Part 1Read the article entitled Atomic Theory I : The Early Days by Anthony Carpi, Ph.D. You may use the link or download the file located at the end of this assignment.
Review Quiz Take this Quiz when you are ready Atomic Theory 1 Quiz Access Code: MA94L |
Review for Unit 5 Test: Part 2Read the second article entitled Atomic Theory II: Ions, Isotopes and Electron Shells by Anthony Carpi, Ph.D.
Do the 'Bohrs Atom: Quantum Behavior in Hydrogen' simulation. Review Quiz Take this Quiz when you are ready Atomic Theory 2 Qu |

|
| Atomic Theory Article by Anthony Carpi Ph.D. | |
| File Size: | 36 kb |
| File Type: | doc |
| Simulated Hydrogen and Helium document | |
| File Size: | 55 kb |
| File Type: | doc |

Nuclear Chemistry
Where did all these elements come from?
What about New Elements?Read the following articles on new elements. Annotate the articles and write a summary essay for each.
Search for Element 113 Concluded at Last Chemical Element 114: Heaviest Element Created Scientists Propose New Names for Elements 114 and 116 Nuclear Missing Link Created At Last: element 117 |
Isotope WorksheetsPrint and complete these worksheets on isotopes or fill in the answers and submit the worksheet through this site. Use your book and class notes to complete these worksheets.
Isotope LabBeanium Isotope Lab
|
Isotope Quiz
Access Code: |
||||||||||||||||||||||||
Extra Credit for Unit 5
Choose one of the following projects
Project must be completed and turned in 3 days before the end of the quarter.
April 2nd deadline for extra credit.
Project 1: Museum BookCreate a Museum Book on the Model of the Atom. Follow the power point presentation to construct your museum book. If you would like to you can print out 4 pages of the template to help you create the book. Use the rubric to help you organize the matrial that you will be adding to the project.
|
Project 2: Time Line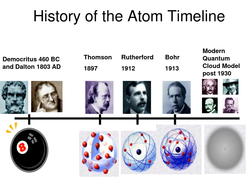
Make a timeline using all of the scientists and discoveries that you have read about. Use your notebook and any other outside resources that you find to create an organized and creative product.
|
||||||||||||